2011年全国硕士研究生招生考试
英语二试题
Section I Use of English
Direction:
Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C or D on ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points)
①The Internet affords anonymity to its users, a blessing to privacy and freedom of speech. ②But that very anonymity is also behind the explosion of cyber-crime that has 1 across the Web.
①Can privacy be preserved 2 bringing safety and security to a world that seems increasingly 3 ?
①Last month, Howard Schmidt, the nation’s cyber-czar, offered the federal government a 4 to make the Web a safer place—a “voluntary trusted identity” system that would be the high-tech 5 of a physical key, a fingerprint and a photo ID card, all rolled 6 one. ②The system might use a smart identity card, or a digital credential 7 to a specific computer, and would authenticate users at a range of online services.
①The idea is to 8 a federation of private online identity systems. ②Users could 9 which system to join, and only registered users whose identities have been authenticated could navigate those systems. ③The approach contrasts with one that would require an Internet driver’s license 10 by the government.
①Google and Microsoft are among companies that already have these “single sign-on” systems that make it possible for users to 11 just once but use many different services.
① 12 , the approach would create a “walled garden” in cyberspace, with safe “neighborhoods” and bright “streetlights” to establish a sense of a 13 community.
①Mr. Schmidt described it as a “voluntary ecosystem” in which “individuals and organizations can complete online transactions with 14 , trusting the identities of each other and the identities of the infrastructure 15 which the transaction runs.”
①Still, the administration’s plan has 16 privacy rights activists. ②Some applaud the approach; others are concerned. ③It seems clear that such a scheme is an initiative push toward what would 17 be a compulsory Internet “driver’s license” mentality.
①The plan has also been greeted with 18 by some computer security experts, who worry that the “voluntary ecosystem” envisioned by Mr. Schmidt would still leave much of the Internet 19 . ②They argue that all Internet users should be 20 to register and identify themselves, in the same way that drivers must be licensed to drive on public roads.
1. [A] swept [B] skipped [C] walked [D] ridden
2. [A] for [B] within [C] while [D] though
3. [A] careless [B] lawless [C] pointless [D] helpless
4. [A] reason [B] reminder [C] compromise [D] proposal
5. [A] information [B] interference [C] entertainment [D] equivalent
6. [A] by [B] into [C] from [D] over
7. [A] linked [B] directed [C] chained [D] compared
8. [A] dismiss [B] discover [C] create [D] improve
9. [A] recall [B] suggest [C] select [D] realize
10. [A] released [B] issued [C] distributed [D] delivered
11. [A] carry on [B] linger on [C] set in [D] log in
12. [A] In vain [B] In effect [C] In return [D] In contrast
13. [A] trusted [B] modernized [C] thriving [D] competing
14. [A] caution [B] delight [C] confidence [D] patience
15. [A] on [B] after [C] beyond [D] across
16. [A] divided [B] disappointed [C] protected [D] united
17. [A] frequently [B] incidentally [C] occasionally [D] eventually
18. [A] skepticism [B] tolerance [C] indifference [D] enthusiasm
19. [A] manageable [B] defendable [C] vulnerable [D] invisible
20. [A] invited [B] appointed [C] allowed [D] forced
Section Ⅱ Reading Comprehension
Part A
Directions:
Read the following four texts. Answer the questions after each text by choosing A, B, C, or D. Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET 1. (40 points)
Text 1
①Ruth Simmons joined Goldman Sachs’s board as an outside director in January 2000; a year later she became president of Brown University. ②For the rest of the decade she apparently managed both roles without attracting much criticism. ③But by the end of 2009 Ms. Simmons was under fire for having sat on Goldman’s compensation committee; how could she have let those enormous bonus payouts pass unremarked? ④By February the next year Ms. Simmons had left the board. ⑤The position was just taking up too much time, she said.
①Outside directors are supposed to serve as helpful, yet less biased, advisers on a firm’s board. ②Having made their wealth and their reputations elsewhere, they presumably have enough independence to disagree with the chief executive’s proposals. ③If the sky, and the share price, is falling, outside directors should be able to give advice based on having weathered their own crises.
①The researchers from Ohio University used a database that covered more than 10,000 firms and more than 64,000 different directors between 1989 and 2004. ②Then they simply checked which directors stayed from one proxy statement to the next. ③The most likely reason for departing a board was age, so the researchers concentrated on those “surprise” disappearances by directors under the age of 70. ④They found that after a surprise departure, the probability that the company will subsequently have to restate earnings increases by nearly 20%. ⑤The likelihood of being named in a federal class-action lawsuit also increases, and the stock is likely to perform worse. ⑥The effect tended to be larger for larger firms. ⑦Although a correlation between them leaving and subsequent bad performance at the firm is suggestive, it does not mean that such directors are always jumping off a sinking ship. ⑧Often they “trade up,” leaving riskier, smaller firms for larger and more stable firms.
①But the researchers believe that outside directors have an easier time of avoiding a blow to their reputations if they leave a firm before bad news breaks, even if a review of history shows that they were on the board at the time any wrongdoing occurred. ②Firms who want to keep their outside directors through tough times may have to create incentives. ③Otherwise outside directors will follow the example of Ms. Simmons, once again very popular on campus.
21. According to Paragraph 1, Ms. Simmons was criticized for .
[A] gaining excessive profits [B] failing to fulfill her duty
[C] refusing to make compromises [D] leaving the board in tough times
22. We learn from Paragraph 2 that outside directors are supposed to be .
[A] generous investors [B] unbiased executives
[C] share price forecasters [D] independent advisers
23. According to the researchers from Ohio University, after an outside director’s surprise departure, the firm is likely to .
[A] become more stable [B] report increased earnings
[C] do less well in the stock market [D] perform worse in lawsuits
24. It can be inferred from the last paragraph that outside directors .
[A] may stay for the attractive offers from the firm
[B] have often had records of wrongdoings in the firm
[C] are accustomed to stress-free work in the firm
[D] will decline incentives from the firm
25. The author’s attitude toward the role of outside directors is .
[A] permissive [B] positive [C] scornful [D] critical
Text 2
①Whatever happened to the death of newspapers? ②A year ago the end seemed near. ③ The recession threatened to remove the advertising and readers that had not already fled to the internet. ④Newspapers like the San Francisco Chronicle were chronicling their own doom. ⑤ America’s Federal Trade Commission launched a round of talks about how to save newspapers. ⑥ Should they become charitable corporations? ⑦Should the state subsidize them? ⑧It will hold another meeting soon. ⑨But the discussions now seem out of date.
①In much of the world there is little sign of crisis. ②German and Brazilian papers have shrugged off the recession. ③Even American newspapers, which inhabit the most troubled corner of the global industry, have not only survived but often returned to profit. ④Not the 20% profit margins that were routine a few years ago, but profit all the same.
①It has not been much fun. ②Many papers stayed afloat by pushing journalists overboard. ③The American Society of News Editors reckons that 13,500 newsroom jobs have gone since 2007. ④Readers are paying more for slimmer products. ⑤Some papers even had the nerve to refuse delivery to distant suburbs. ⑥Yet these desperate measures have proved the right ones and, sadly for many journalists, they can be pushed further.
①Newspapers are becoming more balanced businesses, with a healthier mix of revenues from readers and advertisers. ②American papers have long been highly unusual in their reliance on ads. ③Fully 87% of their revenues came from advertising in 2008, according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation & Development (OECD). ④In Japan the proportion is 35%. ⑤Not surprisingly, Japanese newspapers are much more stable.
①The whirlwind that swept through newsrooms harmed everybody, but much of the damage has been concentrated in areas where newspapers are least distinctive. ②Car and film reviewers have gone. ③So have science and general business reporters. ④Foreign bureaus have been savagely cut off. ⑤Newspapers are less complete as a result. ⑥But completeness is no longer a virtue in the newspaper business.
26. By saying “Newspapers like...their own doom” (Para. 1), the author indicates that newspapers .
[A] neglected the sign of crisis [B] failed to get state subsidies
[C] were not charitable corporations [D] were in a desperate situation
27. Some newspapers refused delivery to distant suburbs probably because .
[A] readers threatened to pay less
[B] newspapers wanted to reduce costs
[C] journalists reported little about these areas
[D] subscribers complained about slimmer products
28. Compared with their American counterparts, Japanese newspapers are much more stable because they .
[A] have more sources of revenue [B] have more balanced newsrooms
[C] are less dependent on advertising [D] are less affected by readership
29. What can be inferred from the last paragraph about the current newspaper business?
[A] Distinctiveness is an essential feature of newspapers.
[B] Completeness is to blame for the failure of newspapers.
[C] Foreign bureaus play a crucial role in the newspaper business.
[D] Readers have lost their interest in car and film reviews.
30. The most appropriate title for this text would be .
[A] American Newspapers: Struggling for Survival
[B] American Newspapers: Gone with the Wind
[C] American Newspapers: A Thriving Business
[D] American Newspapers: A Hopeless Story
Text 3
①We tend to think of the decades immediately following World War II as a time of prosperity and growth, with soldiers returning home by the millions, going off to college on the G. I. Bill and lining up at the marriage bureaus.
①But when it came to their houses, it was a time of common sense and a belief that less could truly be more. ②During the Depression and the war, Americans had learned to live with less, and that restraint, in combination with the postwar confidence in the future, made small, efficient housing positively stylish.
①Economic condition was only a stimulus for the trend toward efficient living. ②The phrase “less is more” was actually first popularized by a German, the architect Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, who like other people associated with the Bauhaus, a school of design, emigrated to the United States before World War II and took up posts at American architecture schools. ③These designers came to exert enormous influence on the course of American architecture, but none more so than Mies.
①Mies’s signature phrase means that less decoration, properly organized, has more impact than a lot. ②Elegance, he believed, did not derive from abundance. ③Like other modern architects, he employed metal, glass and laminated wood—materials that we take for granted today but that in the 1940s symbolized the future. ④Mies’s sophisticated presentation masked the fact that the spaces he designed were small and efficient, rather than big and often empty.
①The apartments in the elegant towers Mies built on Chicago’s Lake Shore Drive, for example, were smaller—two-bedroom units under 1,000 square feet—than those in their older neighbors along the city’s Gold Coast. ②But they were popular because of their airy glass walls, the views they afforded and the elegance of the buildings’ details and proportions, the architectural equivalent of the abstract art so popular at the time.
①The trend toward “less” was not entirely foreign. ②In the 1930s Frank Lloyd Wright started building more modest and efficient houses—usually around 1,200 square feet—than the spreading two-story ones he had designed in the 1890s and the early 20th century.
①The “Case Study Houses” commissioned from talented modern architects by California Arts & Architecture magazine between 1945 and 1962 were yet another homegrown influence on the “less is more” trend. ②Aesthetic effect came from the landscape, new materials and forthright detailing. ③In his Case Study House, Ralph Rapson may have mispredicted just how the mechanical revolution would impact everyday life—few American families acquired helicopters, though most eventually got clothes dryers—but his belief that self-sufficiency was both desirable and inevitable was widely shared.
31. The postwar American housing style largely reflected the Americans’ .
[A] prosperity and growth [B] efficiency and practicality
[C] restraint and confidence [D] pride and faithfulness
32. Which of the following can be inferred from Paragraph 3 about the Bauhaus?
[A] It was founded by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe.
[B] Its designing concept was affected by World War II.
[C] Most American architects used to be associated with it.
[D] It had a great influence upon American architecture.
33. Mies held that elegance of architectural design .
[A] was related to large space
[B] was identified with emptiness
[C] was not reliant on abundant decoration
[D] was not associated with efficiency
34. What is true about the apartments Mies built on Chicago’s Lake Shore Drive?
[A] They ignored details and proportions.
[B] They were built with materials popular at that time.
[C] They were more spacious than neighboring buildings.
[D] They shared some characteristics of abstract art.
35. What can we learn about the design of the “Case Study Houses”?
[A] Mechanical devices were widely used.
[B] Natural scenes were taken into consideration.
[C] Details were sacrificed for the overall effect.
[D] Eco-friendly materials were employed.
Text 4
①Will the European Union make it? ②The question would have sounded strange not long ago. ③Now even the project’s greatest cheerleaders talk of a continent facing a “Bermuda triangle” of debt, population decline and lower growth.
①As well as those chronic problems, the EU faces an acute crisis in its economic core, the 16 countries that use the single currency. ②Markets have lost faith that the euro zone’s economies, weaker or stronger, will one day converge thanks to the discipline of sharing a single currency, which denies uncompetitive members the quick fix of devaluation.
①Yet the debate about how to save Europe’s single currency from disintegration is stuck. ② It is stuck because the euro zone’s dominant powers, France and Germany, agree on the need for greater harmonisation within the euro zone, but disagree about what to harmonise.
①Germany thinks the euro must be saved by stricter rules on borrowing, spending and competitiveness, backed by quasi-automatic sanctions for governments that do not obey. ② These might include threats to freeze EU funds for poorer regions and EU mega-projects, and even the suspension of a country’s voting rights in EU ministerial councils. ③It insists that economic co-ordination should involve all 27 members of the EU club, among whom there is a small majority for free-market liberalism and economic rigour; in the inner core alone, Germany fears, a small majority favour French interference.
①A “southern” camp headed by France wants something different: “European economic government” within an inner core of euro-zone members. ②Translated, that means politicians intervening in monetary policy and a system of redistribution from richer to poorer members, via cheaper borrowing for governments through common Eurobonds or complete fiscal transfers. ③ Finally, figures close to the French government have murmured, euro-zone members should agree to some fiscal and social harmonisation: e.g., curbing competition in corporate-tax rates or labour costs.
①It is too soon to write off the EU. ②It remains the world’s largest trading block. ③At its best, the European project is remarkably liberal: built around a single market of 27 rich and poor countries, its internal borders are far more open to goods, capital and labour than any comparable trading area. ④It is an ambitious attempt to blunt the sharpest edges of globalisation, and make capitalism benign.
36. The EU is faced with so many problems that .
[A] it has more or less lost faith in markets
[B] even its supporters begin to feel concerned
[C] some of its member countries plan to abandon euro
[D] it intends to deny the possibility of devaluation
37. The debate over the EU’s single currency is stuck because the dominant powers .
[A] are competing for the leading position
[B] are busy handling their own crises
[C] fail to reach an agreement on harmonisation
[D] disagree on the steps towards disintegration
38. To solve the euro problem, Germany proposed that .
[A] EU funds for poor regions be increased
[B] stricter regulations be imposed
[C] only core members be involved in economic co-ordination
[D] voting rights of the EU members be guaranteed
39. The French proposal of handling the crisis implies that .
[A] poor countries are more likely to get funds
[B] strict monetary policy will be applied to poor countries
[C] loans will be readily available to rich countries
[D] rich countries will basically control Eurobonds
40. Regarding the future of the EU, the author seems to feel .
[A] pessimistic [B] desperate [C] conceited [D] hopeful
Part B
Directions:
Read the following text and answer the questions by finding information from the right column that corresponds to each of the marked details given in the left column. There are two extra choices in the right column. Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points)
Leading doctors today weigh in on the debate over the government’s role in promoting public health by demanding that ministers impose “fat taxes” on unhealthy food and introduce cigarette-style warnings to children about the dangers of a poor diet.
The demands follow comments made last week by the health secretary, Andrew Lansley, who insisted the government could not force people to make healthy choices and promised to free businesses from public health regulations.
But senior medical figures want to stop fast-food outlets opening near schools, restrict advertising of products high in fat, salt or sugar, and limit sponsorship of sports events by fast-food producers such as McDonald’s.
They argue that government action is necessary to curb Britain’s addiction to unhealthy food and help halt spiraling rates of obesity, diabetes and heart disease. Professor Terence Stephenson, president of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, said that the consumption of unhealthy food should be seen to be just as damaging as smoking or excessive drinking.
“Thirty years ago, it would have been inconceivable to have imagined a ban on smoking in the workplace or in pubs, and yet that is what we have now. Are we willing to be just as courageous in respect of obesity? I would suggest that we should be,” said the leader of the UK’s children’s doctors.
Lansley has alarmed health campaigners by suggesting he wants industry rather than government to take the lead. He said that manufacturers of crisps and candies could play a central role in the Change4Life campaign, the centrepiece of government efforts to boost healthy eating and fitness. He has also criticised the celebrity chef Jamie Oliver’s high-profile attempt to improve school lunches in England as an example of how “lecturing” people was not the best way to change their behaviour.
Stephenson suggested potential restrictions could include banning TV advertisements for foods high in fat, salt or sugar before 9 pm and limiting them on billboards or in cinemas. “If we were really bold, we might even begin to think of high-calorie fast food in the same way as cigarettes—by setting strict limits on advertising, product placement and sponsorship of sports events,” he said.
Such a move could affect firms such as McDonald’s, which sponsors the youth coaching scheme run by the Football Association. Fast-food chains should also stop offering “inducements” such as toys, cute animals and mobile phone credit to lure young customers, Stephenson said.
Professor Dinesh Bhugra, president of the Royal College of Psychiatrists, said: “If children are taught about the impact that food has on their growth, and that some things can harm, at least information is available up front.”
He also urged councils to impose “fast-food-free zones” around schools and hospitals—areas within which takeaways cannot open.
A Department of Health spokesperson said: “We need to create a new vision for public health where all of society works together to get healthy and live longer. This includes creating a new ‘responsibility deal’ with business, built on social responsibility, not state regulation. Later this year, we will publish a white paper setting out exactly how we will achieve this.”
The food industry will be alarmed that such senior doctors back such radical moves, especially the call to use some of the tough tactics that have been deployed against smoking over the last decade.
|
[A] “fat taxes” should be imposed on fast-food producers such as McDonald’s. |
|
|
41. Andrew Lansley held that |
[B] the government should ban fast-food outlets in the neighborhood of schools. |
|
42. Terence Stephenson agreed that |
[C] “lecturing” was an effective way to improve school lunches in England. |
|
43. Jamie Oliver seemed to believe that |
[D] cigarette-style warnings should be introduced to children about the dangers of a poor diet. |
|
44. Dinesh Bhugra suggested that |
[E] the producers of crisps and candies could contribute significantly to the Change4Life campaign. |
|
45. A Department of Health spokesperson proposed that |
[F] parents should set good examples for their children by keeping a healthy diet at home. |
|
[G] the government should strengthen the sense of responsibility among businesses. |
Section Ⅲ Translation
46. Directions:
In this section there is a text in English. Translate it into Chinese. Write your translation on ANSWER SHEET 2. (15 points)
Who would have thought that, globally, the IT industry produces about the same volume of greenhouse gases as the world’s airlines do — roughly 2 percent of all CO₂ emissions?
Many everyday tasks take a surprising toll on the environment. A Google search can leak between 0.2 and 7.0 grams of CO₂, depending on how many attempts are needed to get the “right” answer. To deliver results to its users quickly, then, Google has to maintain vast data centres around the world, packed with powerful computers. While producing large quantities of CO₂, these computers emit a great deal of heat, so the centres need to be well air-conditioned, which uses even more energy.
However, Google and other big tech providers monitor their efficiency closely and make improvements. Monitoring is the first step on the road to reduction, but there is much more to be done, and not just by big companies.
Section IV Writing
Part A
47. Directions
Suppose your cousin Li Ming has just been admitted to a university. Write him/her a letter to
1) congratulate him/her, and
2) give him/her suggestions on how to get prepared for university life.
You should write about 100 words on ANSWER SHEET 2.
Do not sign your own name at the end of the letter. Use “Zhang Wei” instead.
Do not write the address. (10 points)
Part B
48. Directions
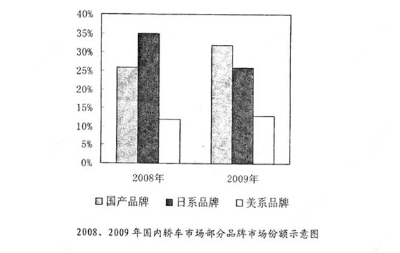
Write an essay based on the following chart. In your writing, you should
1) interpret the chart and
2) give your comments
You should write at least 150 words.
Write your essay on ANSWER SHEET 2. (15points)










暂无评论内容